Diode
•A diode is a 2 lead semiconductor that acts as a one way gate to electron flow.
– Diode allows current to pass in only one direction.
•A pn-junction diode is formed by joining together n-type and p-type silicon.
•In practice, as the n-type Si crystal is being grown, the process is abruptly altered to grow p-type Si crystal. Finally, a glass or plastic coating is placed around the joined crystal.
•The p-side is called anode and the n-side is called cathode.
•When the anode and cathode of a pn-junction diode are connected to external voltage such that the potential at anode is higher than the potential at cathode, the diode is said to be forward biased.
–In a forward-biased diode current is allowed to flow through the device.
•When potential at anode is smaller than the potential at cathode, the diode is said to be reverse biased. In a reverse-biased diode current is blocked.
Diode: How it Works —I
•When a diode is connected to a battery as shown, electrons from the n-side and holes from the p-side are forced toward the center by the electrical field supplied by the battery. The electrons and holes combine causing the current to pass through the diode. When a diode is arranged in this way, it is said to be forward-biased.
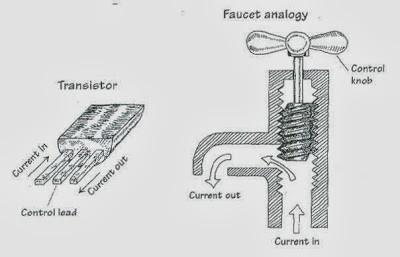
A three lead semiconductor device that acts as: – an electrically controlled switch, or
– a current amplifier.
• Transistor is analogous to a faucet.
–Turning faucet’s control knob alters the flow rate of water coming out from the faucet.
–A small voltage/current applied at transistor’s control lead controls a larger current flow through its other two leads.
Transistor Types: BJT, JFET, and MOSFET
• Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)
– NPN and PNP
• Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET)
– N-channel and P-channel
• Metal Oxide Semiconductor FET (MOSFET)
– Depletion type (n- and p-channel) and enhancement type (n- and p-channel)
BJT Types
• NPN and PNP.
–NPN: a small input current and a positive voltage applied @ its base (with VB>VE) allows a large current to flow from collector to emitter.
–PNP: a small output current and a negative voltage @ its base (with VB<VE) allows a much larger current to flow from emitter to collector.






No comments:
Post a Comment